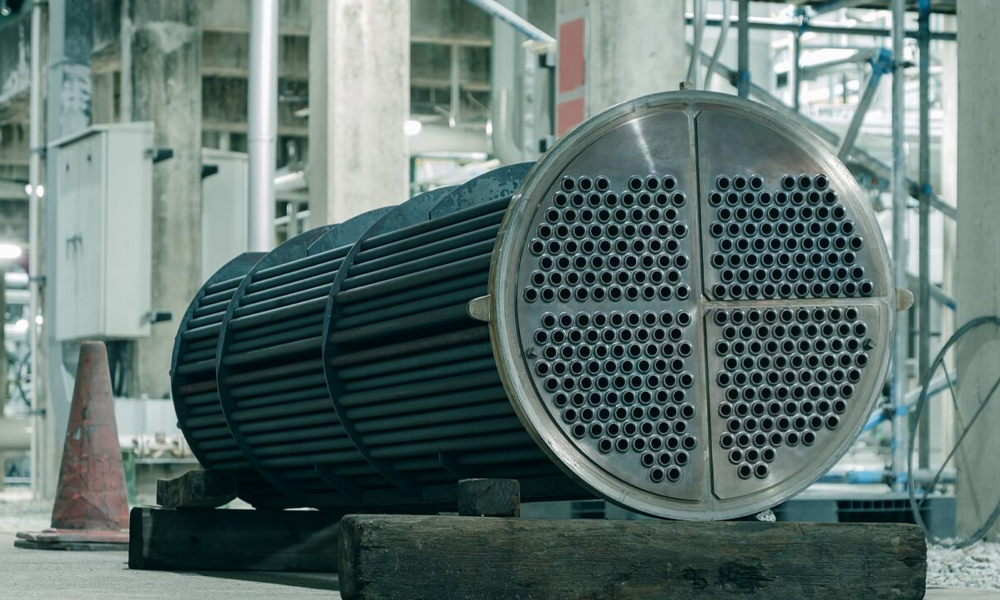
Shell and tube heat exchangers are among the most widely used and critical process equipment in the oil, gas, petrochemical, power, pharmaceutical, and food industries. Due to their ability to withstand high pressure and temperature and effectively transfer heat between various fluids, they hold a prominent position in industrial processes.
Despite their robust design and adherence to international standards, these units may experience failures over time, affecting efficiency, safety, and operational stability. Petrosazeh Beinolmelal Aram Company (Petrosazeh), as one of the leading manufacturers of shell and tube heat exchangers in Iran, presents in this article a scientific and practical analysis of the most common failures in these systems, along with engineering solutions for their prevention.
1. Corrosion: The Hidden Threat to Performance
Corrosion is one of the primary causes of damage in shell and tube heat exchangers. This phenomenon typically occurs due to the exposure of metals to corrosive fluids (such as seawater, acids, or substances containing chloride and sulfur) and electrochemical reactions.
Common Types of Corrosion:
- Uniform Corrosion
- Pitting
- Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC)
- Galvanic Corrosion
Solutions:
- Selection of suitable materials like 316L, nickel alloys, and titanium
- Application of epoxy or ceramic coatings in critical areas
- Injection of corrosion inhibitors into the process fluid
- Regular NDT inspections
Petrosazeh Co. provides precise engineering consultation for material selection, helping to reduce corrosion-related costs and extend the service life of exchangers.
2. Fouling and Blockage: Hidden Efficiency Loss
The formation of mineral deposits, suspended solids, or biological sludge in tubes and channels can hinder heat transfer, increase pressure drop, reduce efficiency, and even cause structural damage.
Main Causes of Fouling:
- Poor quality process water
- Reduced fluid velocity
- High wall temperatures
- Ineffective fluid filtration
Solutions:
- Designing for optimal flow velocities (3–5 fps)
- Installing inlet filters and pre-treatment systems
- Using anti-fouling baffle configurations
- Implementing regular chemical or mechanical cleaning programs
Petrosazeh manufactures exchangers with anti-fouling designs that minimize deposit formation through optimized tube and baffle arrangements.
3. Tube and Connection Leakage: A Process Safety Hazard
Leaks at tube connections, tube sheets, or gaskets can lead to fluid mixing, efficiency loss, contamination, and even complete operational shutdown.
Common Causes of Leakage:
- Localized corrosion in tubes
- Improper welding or tube expansion
- Gasket degradation
- Stress cracks in the tube sheet
Solutions:
- Accurate welding with NDT and hydrostatic testing
- Use of chemically and thermally resistant gaskets
- Annual inspection of critical joints
- Retubing in case of widespread tube failure
Petrosazeh minimizes leakage risk by employing advanced welding technologies and stringent quality control.
4. Vibrations and Mechanical Damage: Structural Disruption
Flow-induced vibrations, especially in the shell side, can lead to tube collision, cracking, or even complete tube rupture if not properly addressed in design.
Main Causes:
- High fluid velocity in the shell side
- Poor baffle or tube layout design
- Improper exchanger installation
Solutions:
- Design in compliance with TEMA Class R and Aspen B-JAC software
- Optimal baffle spacing and use of seal strips
- Periodic inspections for wear, vibration, or tube deformation
Petrosazeh’s exchangers are engineered and dynamically tested to ensure high resistance to vibration and mechanical stress.
5. Steam Hammer and Water Hammer: Destructive Pressure Surges
Water hammer or steam hammer occurs due to sudden flow stoppage or rapid temperature changes, generating momentary high-pressure shocks that can damage the exchanger.
Consequences:
- Tube or shell cracking
- Gasket failure
- Sudden bundle collapse
Solutions:
- Installation of safety valves, pilot valves, and drain valves
- Proper venting and steam discharge line design
- Controlled temperature and pressure ramping
Petrosazeh incorporates dampers and air release chambers in its designs to counter dynamic phenomena.
6. Pressure Drop and Reduced Heat Transfer Efficiency
An increase in pressure drop within the petroleum heat exchanger is often an early indicator of internal problems such as fouling, blockage, or suboptimal design, directly impacting energy consumption and heat transfer performance.
Causes of Pressure Drop:
- Poor tube arrangement
- Overly dense or poorly cut baffles
- Mismatch between actual and design fluid properties
Solutions:
- Customized design based on accurate fluid properties
- Selecting triangular or square tube patterns based on the process
- Monitoring with pressure and flow sensors
Petrosazeh uses precision design software and CFD analysis to deliver products with minimal pressure drop and maximum efficiency.
7. Importance of Scheduled Inspection and Maintenance
Planned inspection and maintenance are among the most effective ways to prevent unexpected failures. Without these practices, even high-quality equipment may degrade quickly.
Recommended Methods:
- Hydrostatic testing
- NDT techniques such as UT, RT, PT
- Visual inspection of tubes and shell
- Regular cleaning with suitable chemicals
Petrosazeh recommends complete servicing of exchangers every 6,000 operating hours or every two years to ensure equipment safety and longevity.
8. Role of Material Selection in Durability and Performance
Selecting the right material is crucial in preventing common failures. Depending on the fluid type, temperature, pressure, and environmental conditions, various materials are used:
Recommended Choices:
- Stainless steel 304/316L for general corrosion resistance
- Inconel or Hastelloy for corrosive fluids
- Titanium for seawater contact
- Copper and brass for low-temperature applications
Petrosazeh assists clients in choosing the most suitable and cost-effective materials tailored to process conditions.
9. The Role of Engineering Design in Reducing Failures
Accurate design is the first line of defense against failure. Key parameters such as:
- Tube layout (Triangular or Square)
- Baffle spacing and angle
- Type of gasket and tube sheet
must be optimized to prevent issues such as vibration, pressure drop, or fouling. Petrosazeh utilizes thermal and mechanical design software to deliver solutions that enhance both efficiency and service life.
Conclusion
While shell and tube heat exchangers are robustly designed, they can experience performance degradation and failures due to corrosion, fouling, leakage, vibration, and steam hammer. Petrosazeh Beinolmelal Aram Company (IPS) manufactures exchangers in compliance with TEMA and ASME standards and offers expert consultation, design, maintenance, and repair services to help clients improve system stability and efficiency.
By implementing regular inspection programs, using suitable materials, adopting precise designs, and training technical personnel, most common failures can be effectively prevented, significantly extending equipment life.







