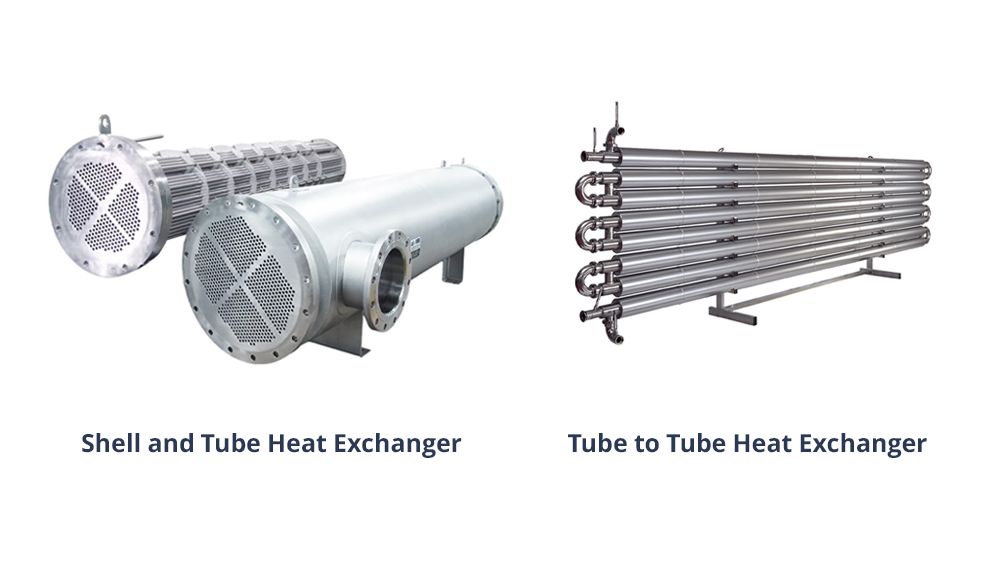
Heat exchangers are at the heart of many industrial processes; from refineries and petrochemical plants to HVAC systems, all rely on these devices to transfer heat between fluids. Petrosazeh Beinolmelal Aram Co. (Petrosazeh), as one of the reputable manufacturers of heat exchangers in Iran, offers a wide range of products for various industries by leveraging advanced technology and international standards. In this article, we will explore the key differences between two commonly used types of heat exchangers—Double Pipe and Shell & Tube—and examine the features, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of each, to help you choose the most suitable option for your industrial project.
What is a Heat Exchanger?
A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat from one fluid to another without mixing them. Depending on the design, this heat transfer occurs through indirect contact via a metallic medium (such as a pipe wall or metal plates). Heat exchangers are used in heating and cooling systems, energy recovery, steam condensers, and many other industrial processes.
Introduction to Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
Structure
A Double Pipe Heat Exchanger, also known as a “Double Pipe,” consists of two concentric pipes. The hot fluid typically flows through the inner pipe, while the cold fluid moves in the opposite or same direction in the annular space between the inner and outer pipes. This simple and compact design makes it highly suitable for low to medium capacities.

Advantages
- Simple Design: Easy to install, operate, and maintain.
- Lower Cost: Fewer components and simpler manufacturing process result in lower overall costs.
- Ideal for Limited Spaces: Due to its smaller size, it is perfect for projects with space constraints.
- Scalability: Multiple units can be installed in series or parallel to increase heat transfer capacity.
Limitations
- Lower Heat Transfer Surface Area: Limited capacity for heat exchange.
- Not Designed for High Pressure/Temperature: May perform poorly under extreme conditions.
Introduction to Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger
Structure
In this type, a bundle of tubes is housed within a large shell. One fluid flows inside these tubes, while the other flows outside the tubes within the shell. Guide plates called “baffles” are placed inside the shell to control the flow path of the second fluid and enhance heat transfer efficiency.
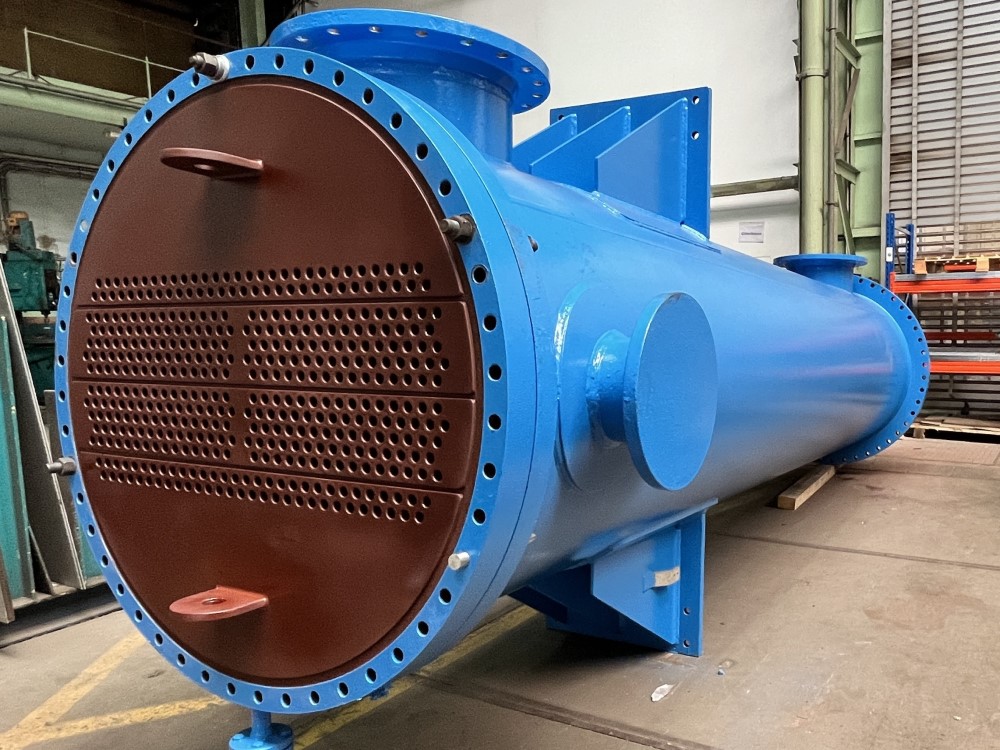

Advantages
- High Heat Transfer Surface Area: Thanks to the large number of tubes and the use of baffles, thermal contact is significantly increased.
- Suitable for Harsh Conditions: Ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, essential in industries like oil & gas and power plants.
- Flexible Design: Can utilize U-shaped or straight tubes depending on project requirements.
Limitations
- More Complex Design & Manufacturing: Engineering complexity is higher compared to tube to tube heat exchangers.
- Larger Installation Space Required: Needs more space for operation.
- Higher Initial Cost: Design, production, and installation costs are greater.
Structural and Design Comparison
Double Pipe Heat Exchanger: With its simple design of just two concentric pipes, it is quicker to manufacture, easier to clean, and offers good installation flexibility.
Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger: More complex, with a multilayer structure and baffles, requiring precise design and engineering calculations.
Heat Transfer Capacity
In Double Pipe exchangers, heat transfer is relatively limited due to the smaller surface area (single inner pipe). However, Shell and tube heat exchangers significantly increase the heat exchange surface through multiple tubes and cross-flow or spiral flow paths. In projects requiring large-scale heat transfer—such as steam condensers in power plants—the Shell & Tube exchanger is undoubtedly the better choice.
Industrial Applications
Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
- HVAC Systems
- Electronic Equipment Cooling
- Swimming Pool Heating
- Small-Scale Food Industries
- Projects with Budget Constraints or Short Lead Times
Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger
- Refineries
- Petrochemical, Oil & Gas Industries
- Power Plants
- Steel and Paper Industries
- Industrial Refrigeration Systems
Maintenance and Repair
Double Pipe Heat Exchanger: Due to its simple structure, it is easy to disassemble, clean, and descale, with lower maintenance costs.
Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger: Although more complex, with proper design (such as removable bundles), maintenance can be effectively managed. Petrosazeh designs these exchangers so that even if part of the tube bundle fails, it can be easily replaced.
Pressure Drop
In applications where maintaining system pressure is critical, the straight flow path of tube to tube heat exchangers results in lower pressure drops. Conversely, the complex flow patterns in Shell & Tube exchangers may cause higher pressure drops, although this can be controlled through proper baffle design.
Economic Considerations
While Double Pipe exchangers have a lower initial cost, they may become inefficient for large-scale projects in the long term. On the other hand, Shell & Tube exchangers, despite their higher initial investment, offer longer service life and higher efficiency, resulting in long-term savings. Petrosazeh offers cost-effective solutions for both types, tailored to customers’ budgets and requirements.
Choosing the Right Heat Exchanger
The choice between these two types entirely depends on project conditions. If your project is small-scale, with low fluid flow, and has space and budget constraints, the Double Pipe exchanger is the best option. However, for applications involving large fluid volumes, high pressures and temperatures, and a need for high thermal efficiency, the Shell & Tube exchanger is the clear choice.
Compliance with Standards
Petrosazeh adheres to international standards such as ASME and TEMA in the design and production of both types of exchangers. This not only ensures manufacturing quality but is also a safety requirement in sensitive industries like petrochemicals.
Future of Heat Exchangers in Iran
With the growing need for energy optimization in industries and the expansion of industrial projects, the demand for high-efficiency heat exchangers is increasing. Petrosazeh is investing in R&D to manufacture exchangers that consume less energy, have a longer lifespan, and are environmentally friendly. Moreover, domestic production of these products reduces dependency on imports and strengthens the national industry.
Conclusion
Heat exchangers play a vital role in many industrial processes. Choosing between Double Pipe and Shell & Tube exchangers requires a careful assessment of factors such as capacity, pressure, temperature, space, cost, and maintenance. With extensive experience and a skilled engineering team, Petrosazeh is ready to offer the best solutions for various industries.
For expert consultation and choosing the right heat exchanger, contact the specialists at Petrosazeh Beinolmelal Aram (IPS).