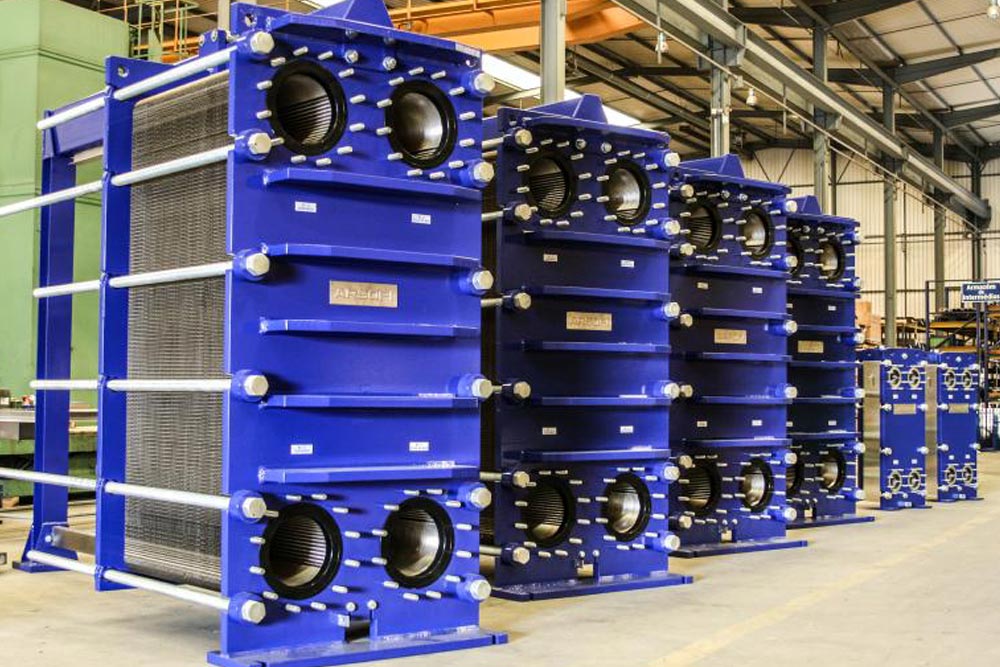
Heat exchangers are key components in refineries, playing a vital role in heat transfer between fluids at different temperatures. Proper installation and commissioning of these devices not only ensures optimal performance of refining processes but also enhances safety, extends equipment life, and improves energy efficiency. This article provides a comprehensive review of the installation steps, technical considerations, challenges, and solutions related to the commissioning of heat exchangers in refineries.
Importance of heat exchangers in refineries
Heat exchangers are used in processes such as heating, cooling, condensation, and evaporation of process fluids, and they play a critical role in operations like crude oil distillation, steam production, and hydrocarbon cooling. Without the proper function of these exchangers, refining processes can experience efficiency losses, increased energy consumption, and even production shutdowns. The variety of heat exchanger designs, such as shell-and-tube or plate exchangers, and their wide applications, require careful attention when selecting and installing these devices. Any installation errors can lead to issues such as leakage, fouling, corrosion, or even safety incidents. Therefore, adhering to technical details and industry standards is mandatory.
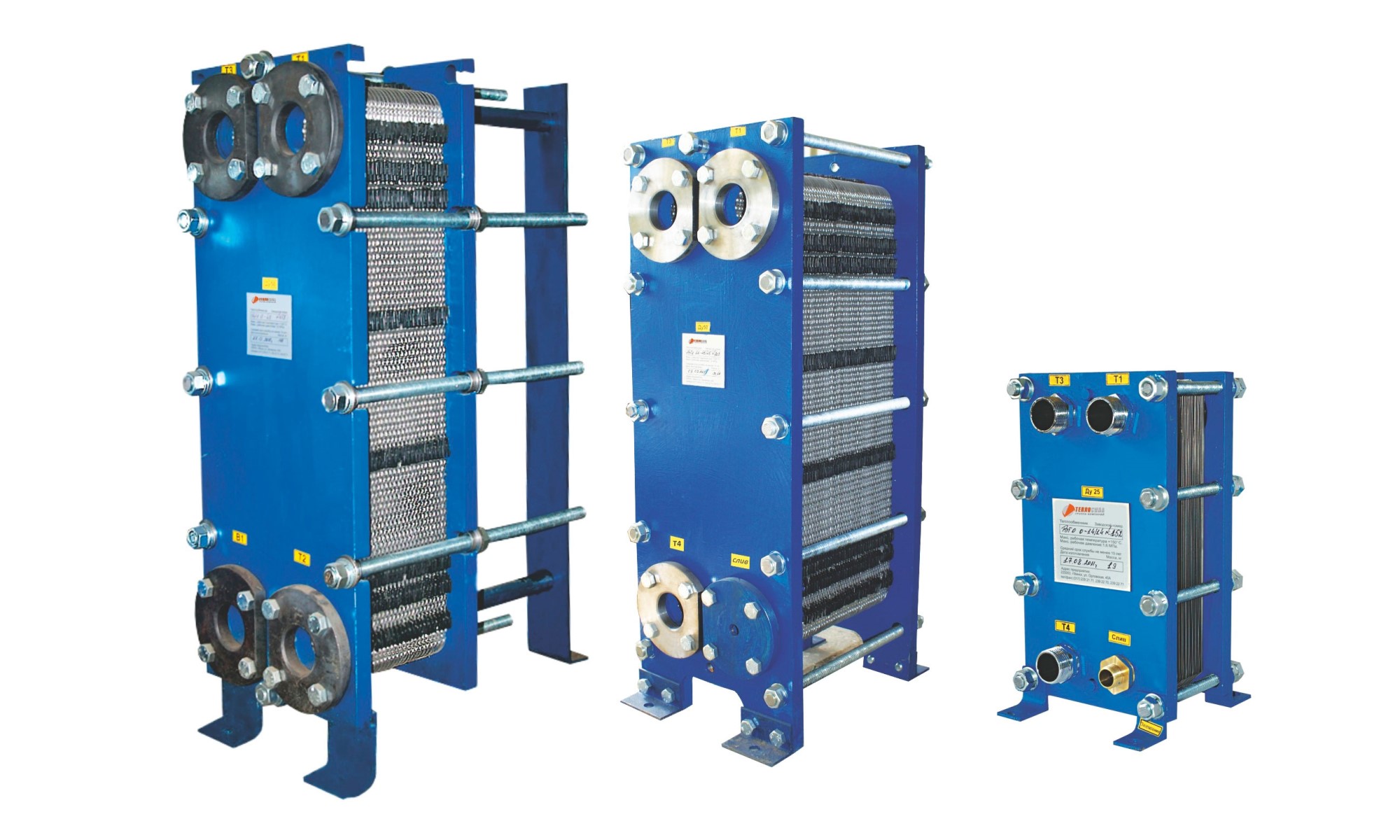

Also read: Uses of plate heat exchangers in oil & gas refineries
Choosing the right location for heat exchanger installation
Choosing the appropriate location for heat exchanger installation is the first step in the commissioning process. The location should provide easy access for maintenance and repair operations, adequate ventilation, and sufficient space for piping and other connections. Additionally, the installation site should be free from sources of excessive vibration or adverse environmental conditions such as high humidity or dust. In refinery environments, where high temperatures and corrosive chemicals are common, care must be taken to ensure the exchanger is not exposed to direct contact with these factors. For example, in shell and tube heat exchangers, sufficient space should be allocated for the removal of the tube bundle during maintenance. Installation should be carried out on strong, level foundations, and the chosen site must comply with refinery safety standards such as API and ASME. Close cooperation with the piping and civil teams and careful review of engineering drawings will help prevent potential problems.
Preparation before installation
Before beginning installation, the technical specifications of the heat exchanger must be thoroughly reviewed to ensure that the delivered equipment meets the process requirements. This review includes evaluating the working pressure and temperature, the type of process fluids, and the material composition of the exchanger. For corrosive fluids, selecting resistant alloys such as stainless steel is essential. Additionally, a physical inspection of the body, tubes, plates, and seals of the exchanger must be conducted to identify any potential damage. Initial cleaning of the equipment to remove contaminants or residues from manufacturing and transportation is also crucial, as these impurities can cause blockages and reduce the efficiency of the exchanger. Preparing necessary tools, such as cranes, leveling instruments, welding equipment, and carefully planning the sequence of installation steps, along with full coordination among teams, is essential for successful installation operations.
Heat exchanger installation steps
In the installation process, the heat exchanger must first be carefully placed on the supporting foundations and leveled. Improper leveling can lead to unwanted stress on the exchanger structure or uneven fluid flow distribution. Once the exchanger is stabilized, the inlet and outlet pipes are connected. These connections must be made according to industry standards using high-quality flanges, seals, and bolts. The fluid flow direction must be precisely followed as per the design to ensure optimal heat transfer performance. After completing the installation, a pressure test (Hydrotest) is required to ensure the integrity of the connections and confirm there are no leaks under operating pressure. Finally, the entire system should be purged of air and filled with process fluid to prevent air bubbles from forming, which could disrupt heat transfer.
Initial commissioning and adjustments
The initial commissioning of the heat exchanger must be carried out gradually and in a controlled manner to avoid thermal or pressure shocks to the system. Initially, fluids at lower temperatures and pressures should be introduced to the exchanger, gradually reaching the designed conditions. At this stage, precise monitoring of parameters such as temperature, pressure, and fluid flow is of utmost importance. Necessary adjustments should be made based on the actual performance of the exchanger and compared with design data. If unusual pressure drops or unexpected performance are observed, the cause must be identified and corrective actions taken. Correct installation and calibration of temperature and pressure sensors for continuous monitoring are essential, and operators should receive the necessary training for safe and effective operation of the exchanger.
Safety considerations in installation and commissioning
Safety in the installation and commissioning process of heat exchangers is crucial. Before starting work, a risk assessment should be performed to identify potential hazards such as hazardous fluid leaks, explosions, or mechanical damage. All personnel involved must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). During installation, mixing air with flammable gases should be avoided, and if necessary, systems should be purged using inert gases such as nitrogen. Pressure tests should be carried out under close supervision and in accordance with standard safety protocols. Additionally, preparing teams for emergency situations, such as leaks or abnormal pressure increases, along with ensuring easy access to firefighting equipment, is essential for ensuring process safety.
Periodic maintenance and repairs
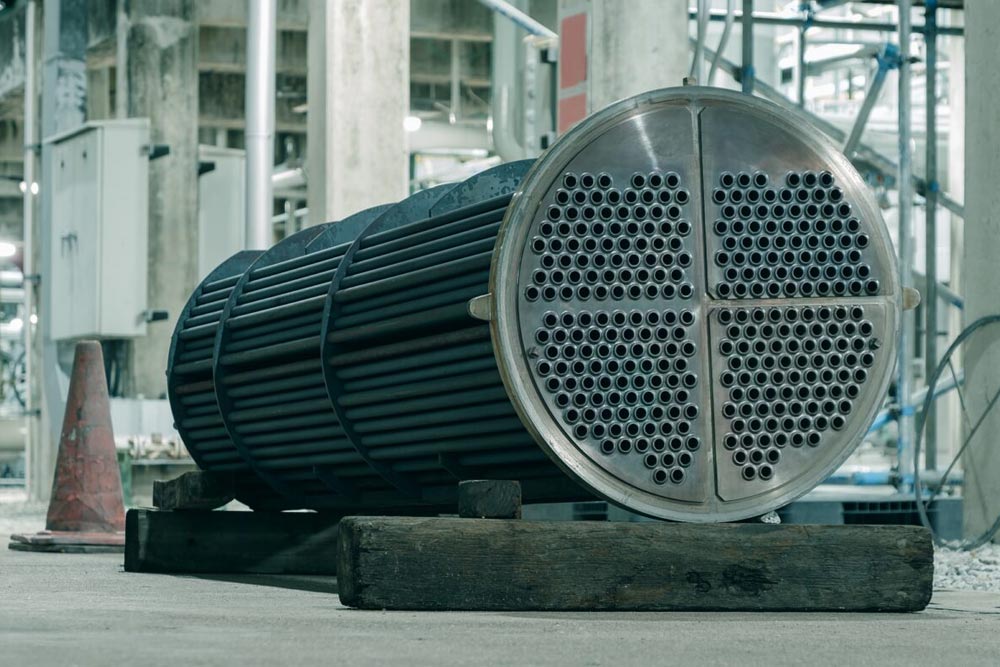
Regular maintenance of heat exchangers plays a key role in maintaining optimal performance and extending refinery equipment life. Fouling and corrosion are common problems that can reduce heat transfer efficiency and increase operational costs. Implementing periodic cleaning programs, using chemical or mechanical methods depending on the type of deposits, is crucial. Regular inspections to detect cracks, leaks, or wear in the various components of the exchanger should be included in the maintenance schedule. In shell-and-tube exchangers, checking the tube bundles and tube sheets is particularly important. Using advanced technologies such as smart sensors and online monitoring systems can help detect problems early and reduce equipment downtime.
Common challenges and solutions
A common challenge in heat exchanger installation is the discrepancy between the initial design and the actual conditions of the installation site. To overcome this problem, a thorough review of drawings and improved coordination between the design and execution teams is necessary. Leakage in connections is another common issue that can be minimized by using appropriate seals and conducting pressure tests before startup. Correctly selecting the type of heat exchanger based on operational conditions, using high-quality fluids, and applying proper filtration can also reduce the risk of fouling and corrosion. Ongoing training for personnel and updating maintenance procedures can play an important role in preventing problems.
Choosing the right heat exchanger type
Selecting the right type of heat exchanger directly impacts the success of refinery projects. Shell-and-tube exchangers are a popular choice in refineries due to their high mechanical strength, ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures, and adaptability to harsh operational conditions. In contrast, plate exchangers are preferred in applications with clean fluids and relatively mild operating conditions due to their higher thermal efficiency and space-saving design. The selection should be based on a thorough analysis of fluid characteristics, temperature, pressure, required capacity, and economic considerations.

Role of modern technologies in installation and operation
Modern technologies play a significant role in improving the installation and operation of heat exchangers. The use of advanced simulation software, such as HTRI or Aspen, allows engineers to model and optimize the exchanger’s performance before actual installation. IoT-based monitoring systems provide real-time tracking of the exchanger’s status and enable early detection of potential issues. These technologies not only increase system efficiency but also help reduce maintenance costs and enhance safety.
Industry standards and certifications
Compliance with industry standards, such as API 660 for shell-and-tube exchangers and ASME Section VIII for the design of pressure equipment, is essential throughout the design, manufacturing, and installation phases. These standards ensure that equipment will perform safely and effectively under harsh operational conditions. Quality certifications, such as ISO 9001, and third-party inspections validate the quality and compliance of equipment, preventing future issues.
Conclusion
Proper installation and commissioning of heat exchangers in refineries is a complex and critical process that requires careful planning, adherence to technical and safety requirements, and the use of modern technologies. Selecting the appropriate location, preparing adequately before installation, ensuring precise installation and gradual commissioning, plays a key role in ensuring optimal performance and extending the life of the exchanger. By implementing regular maintenance programs and utilizing advanced technologies, common challenges can be managed, and the efficiency of refining processes can be enhanced.
References:
- ThomasNet: Heat Exchanger Installation Guidelines
- Chemical Engineering World: Best Practices for Heat Exchanger Installation in Refineries
- WhatIsPiping: Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Installation and Maintenance
- IQS Directory: Industrial Heat Exchangers: Installation and Safety
- Filson Filters: Comprehensive Guide to Heat Exchanger Setup
- Boardman INC: Refinery Heat Exchanger Installation Tips
Read more:







