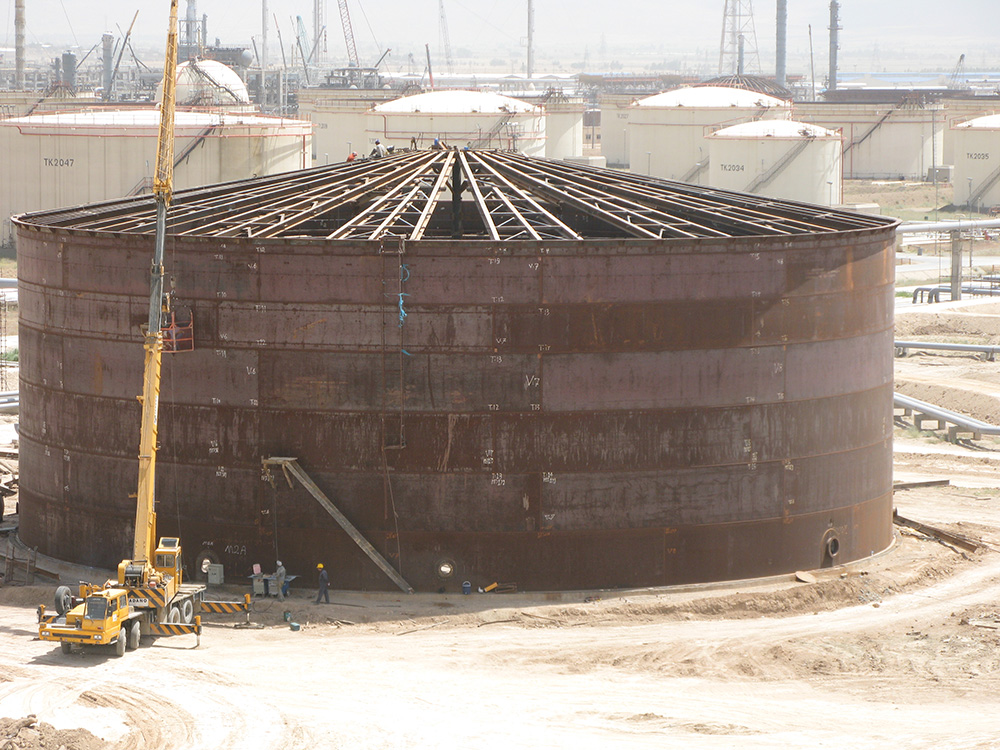
Floating roof cylinder tanks are among the most practical storage equipment in the oil and gas, petrochemical, and other industries. Due to their unique design, they are widely used for managing vapors and minimizing environmental impact. This article examines the types of floating roof tanks and compares internal and external floating roof tanks, exploring the factors affecting their selection.
Types of Floating Roof Cylinder Tanks
Floating roof cylinder tanks are generally divided into two main categories:
Internal Floating Roof Tanks: These tanks combine a fixed and a movable roof. This design minimizes the liquid’s evaporation rate. The floating roof sits within the tank body, directly on the liquid surface, and moves in sync with the liquid level. This design reduces vapor emissions and enhances safety against incidents.
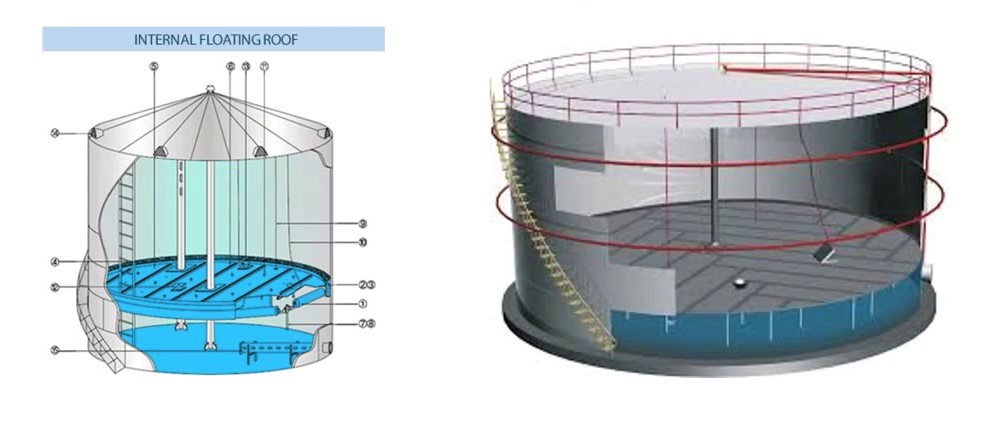
External Floating Roof Tanks: In this type, the tank’s roof is positioned above the liquid surface and changes height as the tank fills or empties. Although this type also largely prevents fluid evaporation, external floating roof tanks are typically used in large-scale projects with high storage volumes.
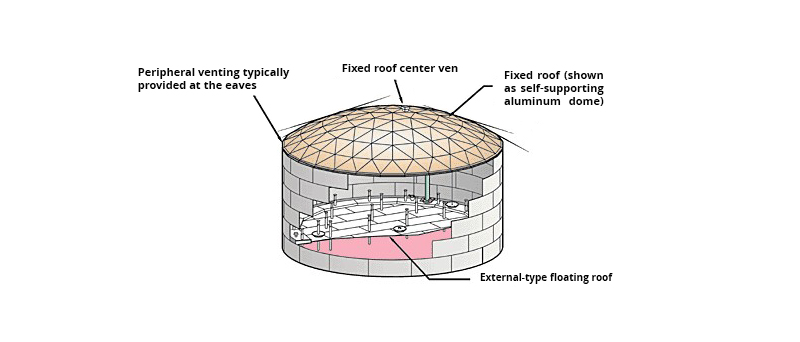
Comparison of Internal and External Tanks
Both tanks are constructed from materials like aluminum and stainless steel, and both—especially internal floating roof tanks—are environmentally friendly, preventing contamination. Economically, the design and construction of both storage tanks are justifiable.
Design and Construction:
Internal roof tanks generally have a simpler design and lower construction costs compared to external floating roof tanks. Additionally, due to the lack of complex infrastructure needs, they are faster and easier to install. However, external floating roof tanks are designed for larger storage volumes and require more precision in construction.
Vapor Control:
Internal floating roof tanks effectively prevent vapor emissions as the roof sits directly on the liquid. This feature is particularly important in petrochemical industries, where vapor emissions are a serious risk. In contrast, external tanks, due to the roof’s higher positioning, may be less effective in vapor control, although modern technology can mitigate these issues. Overall, better vapor containment reduces the risks of fire and toxicity for personnel.
Tank Safety:
In terms of safety, internal tanks, due to reduced vapor emissions, are generally more reliable against fire and explosion. Consequently, internal tanks are preferred in sensitive projects. However, in cases where a large volume of material needs storage, external tanks may be justifiable.
Costs:
Both internal and external floating roof tanks have higher maintenance costs than fixed-roof tanks. Generally, internal floating roof tanks have lower initial costs, but their maintenance costs may increase over time. External tanks, due to their complex structure and need for additional infrastructure, have higher construction and maintenance costs.
Storage in Internal and External Floating Roof Tanks
Floating roof cylinder tanks are commonly used to store various types of liquids and gases. The type of material suitable for storage in each tank depends on the characteristics of the material and the specific design of the tank. Below are common applications for each type:
Internal Floating Roof Tanks
Typically used for:
- Crude Oil: The specific design of these tanks helps reduce vapor production, making them ideal for storing crude oil and other petroleum products.
- Gasoline and Liquid Fuels: Due to fire risk and toxicity from vapors, these tanks are ideal for gasoline and other liquid fuels.
- Petrochemical Products: These tanks can store petrochemical materials, including both light and heavy naphtha.
External Floating Roof Tanks
Suitable for storing:
- Crude Oil and Petroleum Products: Similar to internal tanks, these are also suitable for crude oil and petroleum products, particularly for larger volumes.
- Liquid Gases: Some of these tanks are designed for storing liquid gases, such as propane and butane.
- Chemical Materials: These tanks are useful for storing liquid chemicals, particularly in petrochemical and chemical industries.
Factors Influencing Tank Type Selection
Several important factors should be considered when choosing between internal and external tanks:
- Type of Stored Material: Different chemicals require different storage conditions. For instance, if the material releases toxic vapors, an internal tank may be more suitable.
- Required Storage Volume: For projects requiring high storage volumes, external tanks are a good option.
- Environmental and Site Conditions: In areas where fire or explosion risks are high, internal tanks can reduce these hazards.
- Available Budget: Construction and maintenance costs are key factors in tank selection.
Conclusion
Ultimately, choosing the appropriate floating roof tank depends on the project’s requirements and conditions. While both internal and external tanks play important roles in safe storage and vapor reduction, factors like the type of stored material, required volume, and budget determine the final choice. By carefully assessing each tank’s features and the specific project requirements, the most efficient and economical option can be chosen, increasing storage process safety and efficiency.







