Heat exchangers efficiently transfer heat between two different fluids and play a key role in increasing efficiency and optimizing production processes in many industries, especially in the oil and gas sector. Refineries involve complex processes such as distillation, fluid preheating, and vapor cooling, where heat exchangers—particularly plate heat exchangers—are widely used.
This article explores the applications of plate heat exchangers in the oil and gas industry, highlighting their advantages and challenges. Additionally, the technological and economic benefits of these devices in refinery processes will be discussed in detail.
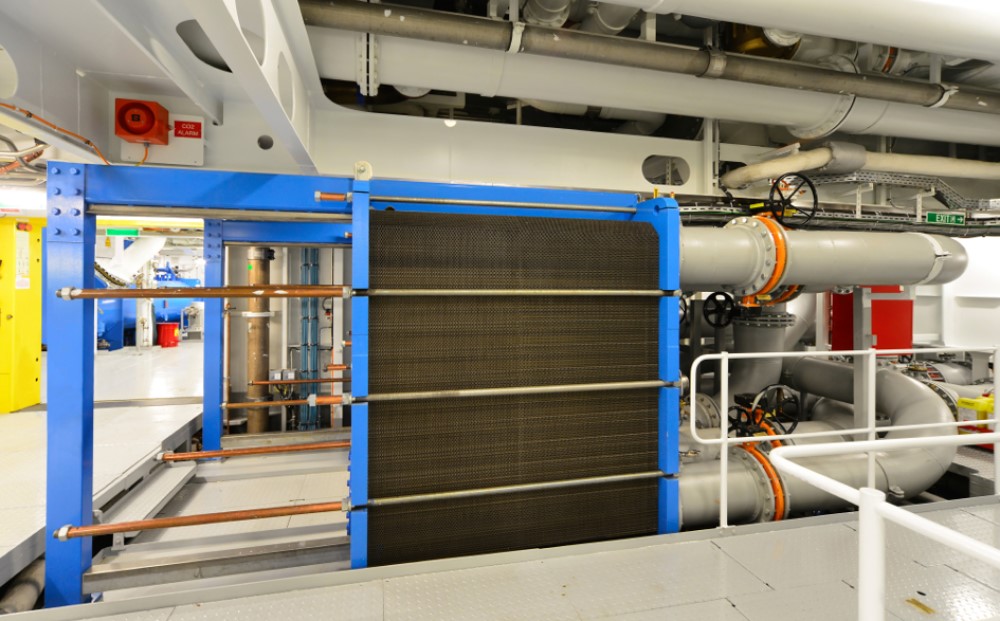
Plate Heat Exchangers: Structure and Function
Plate heat exchangers are devices composed of thin metal plates arranged vertically and horizontally to allow two different fluids (typically one hot and one cold) to pass through the gaps between the plates without mixing. This design increases the contact surface area, thereby enhancing heat transfer efficiency.
Plate heat exchangers offer numerous advantages. Due to their compact and modular design, they can be installed in limited spaces. Additionally, their heat transfer capability is significantly higher than other types of heat exchangers, such as tube to tube exchangers. These characteristics make plate heat exchangers highly valuable in complex industries such as oil and gas.
Applications of Plate Heat Exchangers in Refineries
In refineries, one of the primary applications of plate heat exchangers is heat transfer between different fluids. Some of their key applications include fluid preheating and vapor cooling. In distillation processes, which require precise temperature control, plate heat exchangers effectively maintain temperature and optimize fluid flow.
Another important application of plate heat exchangers in refineries is heat exchange in distillation towers. During this process, fluids at different temperatures flow through the heat exchangers, transferring thermal energy from one fluid to another. This enhances the efficiency of refinery processes while reducing energy costs.
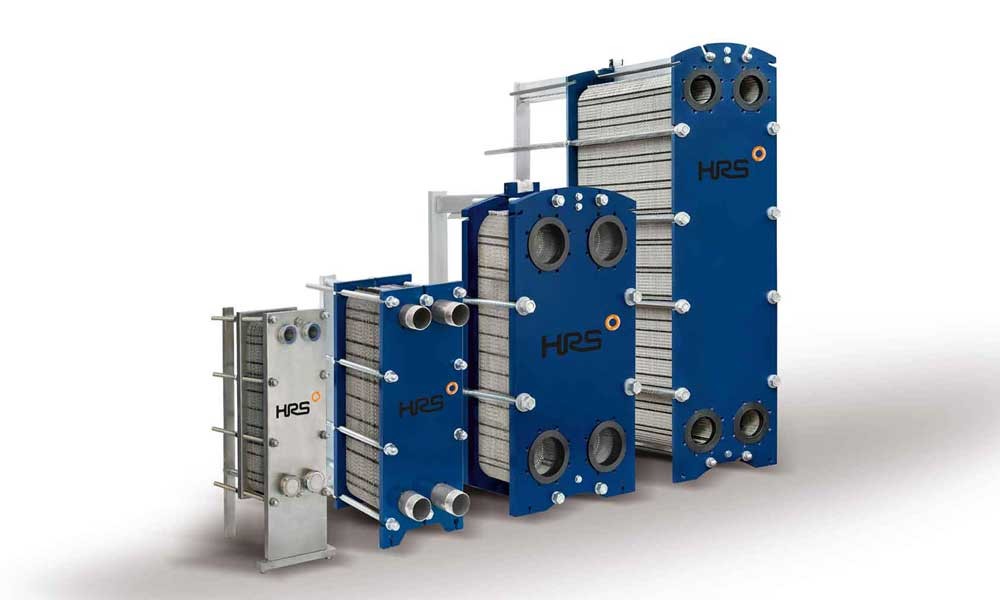

Advantages of Using Plate Heat Exchangers in the Oil & Gas Industry
Plate heat exchangers offer several benefits in the oil and gas industry. The most significant advantage is their high heat transfer efficiency. Due to their specialized design, these exchangers minimize energy losses while transferring heat effectively. This is particularly beneficial when handling fluids with extremely high or low temperatures.
Another major advantage is their compact and modular design, allowing engineers to install them in confined spaces easily. Furthermore, if system capacity needs to be adjusted, additional plates can be added, making them highly flexible for use in refineries and other oil and gas facilities.
Moreover, plate heat exchangers are advantageous in terms of maintenance and servicing. Since their plates can be easily disassembled and cleaned, they require lower maintenance costs compared to other types of heat exchangers.
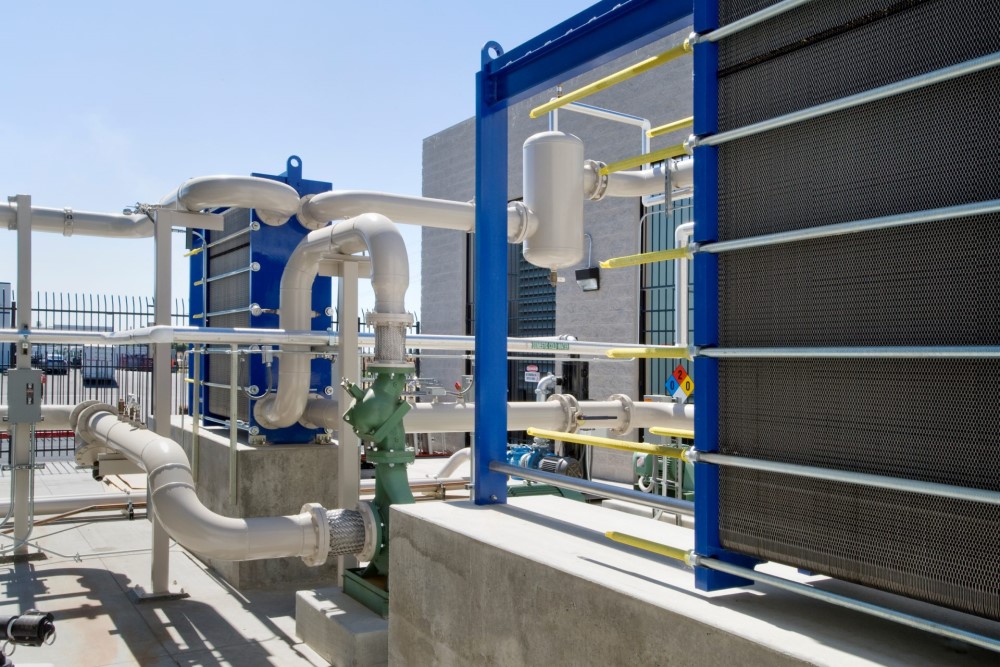

Challenges and Issues in Using Plate Heat Exchangers in the Oil & Gas Industry
Despite their numerous benefits, plate heat exchangers face certain challenges. One common issue is the accumulation of solid deposits on the plates, which can reduce heat transfer efficiency and require frequent cleaning and maintenance.
Corrosion is another major concern, particularly in the oil and gas industry, where fluids often contain corrosive substances. This can damage the exchanger plates and shorten their lifespan. To mitigate these issues, selecting appropriate materials for the plates and considering the chemical composition of the fluids is essential.
Comparison of Plate Heat Exchangers with Other Types
Compared to other types of heat exchangers, such as shell and tube heat exchangers and air cooler heat exchangers, plate heat exchangers offer significant advantages. One of the primary differences is their larger contact surface area, which results in more efficient heat transfer within a smaller space.
While shell and tube heat exchangers are better suited for applications requiring higher capacities, plate heat exchangers are preferred in many industries—especially oil and gas—due to their superior efficiency and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, plate heat exchangers require less space, making them ideal for projects with spatial limitations.
Future of Plate Heat Exchangers in the Oil & Gas Industry
Currently, plate heat exchangers are an essential component of the oil and gas industry, and with ongoing technological advancements, their usage is expected to grow. One emerging trend in this field is the improvement of plate materials to enhance resistance to corrosion and wear.
Furthermore, advancements in software and digital technologies for monitoring and controlling plate heat exchanger performance will contribute to higher operational efficiency and energy savings. Additionally, optimizing refinery processes and incorporating renewable energy sources may significantly impact the design and application of plate heat exchangers in the future.
Conclusion
With their high heat transfer efficiency and compact design, plate heat exchangers play a crucial role in the oil and gas industry. These devices are widely used in refineries to optimize production processes and reduce energy costs. Despite challenges such as fouling and corrosion, the numerous advantages of plate heat exchangers ensure their continued importance in the industry. As technology advances, the adoption of plate heat exchangers is expected to increase, further enhancing refinery efficiency.
References
- Alfa Laval – Plate Heat Exchangers
- Oil & Gas Journal
- Thermal Engineering







