In the oil and gas refining industry, efficiency and cost reduction are of paramount importance, and industrial furnaces are among the key equipment used to provide the necessary heat for chemical processes. Petrosazeh Beinolmelal Aram Co. (Petrosazeh), with years of experience in the design and manufacturing of such equipment, helps refineries select furnaces best suited to their operational and environmental conditions.
It is well known that choosing between vertical and horizontal furnaces has a direct impact on process efficiency, cost, and safety. This article examines the differences between these two types of industrial furnaces from the perspectives of design, performance, cost, and maintenance to determine which performs better under various conditions.
Importance of Furnaces in Refineries
Refinery furnaces are essential for supplying heat in processes such as distillation, cracking, and hydrotreating. These systems heat fluids, allowing the separation and conversion of crude oil into valuable products such as gasoline and diesel.
Petrosazeh manufactures furnaces that distribute heat evenly and minimize energy loss — a crucial feature for large-scale refineries. Precise temperature control ensures proper chemical reactions; for example, in the cracking process, improper temperatures can reduce product quality or cause fouling.
Moreover, furnaces must comply with safety and environmental standards. Optimized designs reduce fuel consumption and pollutant emissions, which ultimately lowers operating costs.
Differences in Design and Structure
Vertical and horizontal furnaces differ structurally in ways that influence their applications and performance.
Vertical industrial furnace: The tubes are positioned upright, and heat flows from the bottom to the top. This design occupies less space and is suitable for refineries with limited land area.

Horizontal industrial furnace: The tubes are laid horizontally, facilitating the flow of heavy fluids and reducing fouling. The structure is simpler and less expensive to manufacture but requires more space. In high-capacity units, access to tubes for maintenance and repair is also easier.
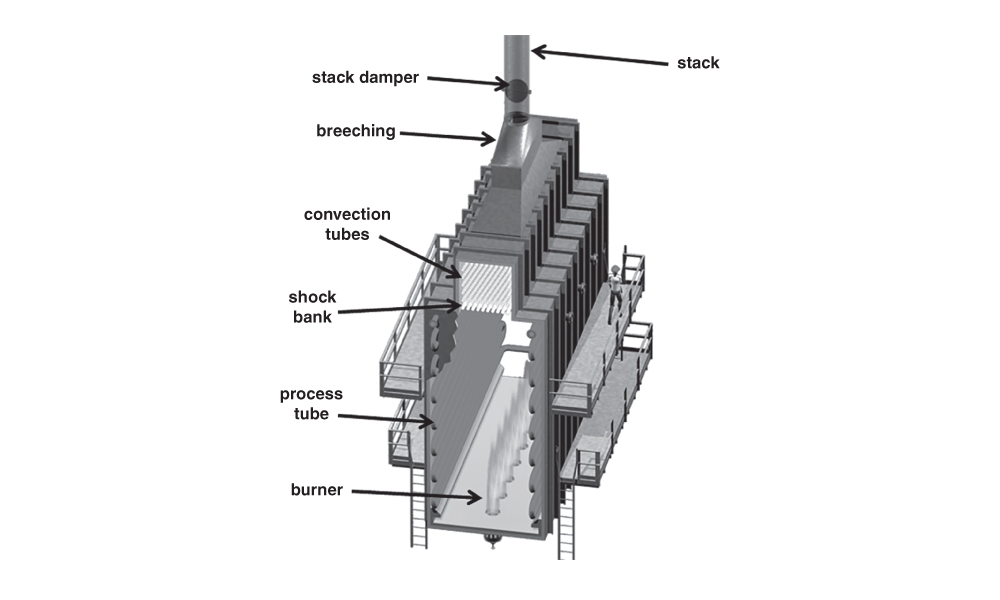
Advantages and disadvantages of vertical furnace design:
- Advantages: Smaller footprint, natural and uniform heat distribution, higher energy efficiency due to natural convection.
- Disadvantages: More complex construction, more difficult installation, requires more durable materials.
Advantages and disadvantages of horizontal furnace design:
- Advantages: Easier maintenance and repair access, suitable for heavy and fouling-prone fluids.
- Disadvantages: Requires more space, and heat distribution is less uniform than in vertical furnaces, potentially affecting efficiency in sensitive processes.
Efficiency and Heat Distribution
A vertical furnace provides more uniform heat distribution because the heat naturally rises from bottom to top. This reduces energy consumption and is ideal for temperature-sensitive processes such as hydrocracking.
A horizontal furnace offers less uniform heat distribution but performs better with high-density fluids and prevents sediment buildup. It is suitable for heavy processes like refining high-viscosity crude oil.
Furthermore, the compact structure of vertical furnaces makes them less susceptible to environmental vibrations, ensuring better long-term efficiency. Conversely, horizontal furnaces may require additional adjustments to maintain heat distribution, especially when variable fuels are used.
Ultimately, furnace efficiency depends on the fluid type, fuel, and system design. Proper selection can reduce energy consumption by up to 15% and improve overall performance.
Comparison of Construction and Installation Costs
The construction cost of a vertical furnace is typically higher due to its more complex design and need for stronger materials. However, these furnaces are more economical in the long term because they save both space and energy.
Horizontal furnaces cost less to build due to their simpler structure and easier fabrication process. However, their larger footprint can increase installation costs in expensive land areas, making them more suitable for projects with limited budgets.
Cost-related factors:
- Vertical furnace: More expensive materials, complex installation, space savings.
- Horizontal furnace: Lower fabrication cost, faster installation, requires more land area.
Additionally, installing a vertical furnace takes longer due to the need for stronger foundations and more precise engineering. In contrast, horizontal furnaces are quicker to install and easier to maintain. The final choice depends on project budget and available space.
Maintenance and Repairs
Maintenance of vertical furnaces can be more challenging due to limited access to tubes; however, their compact design generally reduces the need for frequent repairs. Horizontal furnaces, on the other hand, offer better accessibility, making cleaning and repairs easier — a major advantage in refineries where heavy fouling occurs. However, they may be more prone to corrosion due to greater exposure to environmental conditions.
Vertical furnaces experience less fouling because of natural upward heat flow, whereas horizontal furnaces require more frequent cleaning to maintain efficiency.
Specific Applications of Each Furnace Type
Vertical industrial furnaces are better suited for processes requiring uniform temperature and precise control, such as hydrotreating. Their small footprint makes them popular in modern refineries with limited space.
Horizontal industrial furnaces perform better in high-capacity processes such as heavy oil cracking, as horizontal fluid flow is more effective for dense fluids. They are commonly used in larger units.
Applications summary:
- Vertical furnace: Hydrotreating, gas processing, compact refineries.
- Horizontal furnace: Heavy oil cracking, crude oil refining, large-scale units.
Environmental Impact
Vertical furnaces, with higher efficiency, consume less fuel and emit fewer pollutants a crucial factor for environmentally regulated refineries.
Horizontal furnaces may consume more fuel, but advanced burner technology and precise control systems can reduce emissions significantly.
Properly designed systems of either type can contribute to environmental sustainability, though vertical furnaces generally offer superior environmental performance.
Conclusion
Differences in design, efficiency, cost, and maintenance make the choice between vertical and horizontal furnaces dependent on project needs and process type.
Vertical furnaces, with their compact size, higher energy efficiency, and more uniform performance, are ideal for space-limited and temperature-sensitive units. In contrast, horizontal furnaces, with lower construction costs and easier maintenance, are practical and economical solutions for heavy-duty, high-capacity processes.
Ultimately, the optimal choice is achieved when furnace engineering aligns with the nature of the process fluid, available space, and the project’s economic objectives.
References:
- xrgtechnologies.com/what-is-a-fired-heater-for-dummies/
- teinstruments.com/horizontal-versus-vertical-furnace-arrangement/
- petro-online.com/news/analytical-instrumentation/11/breaking-news/how-are-furnaces-used-for-analysis/56015/
- patents.google.com/patent/US4986222A/en/
- saftherm.com/news/company-news/differences-vertical-tube-furnace-and-horizontal-tube-furnaces/
- crystec.com/kllcompe.htm/
- superbheating.com/info/what-is-the-difference-between-horizontal-and-102941078.html/







