Tube to tube heat exchanger is among the most widely used device in the oil and gas industries. This heat exchanger is responsible for transferring heat between two fluids, where in most cases, one fluid is a process gas or liquid, and the other is an intermediary fluid such as water or oil. The design of tube to tube heat exchangers allows the fluid flows to pass through two separate pathways in different tubes, with no direct contact between them. Heat transfer occurs through the tube walls, which helps reduce energy loss and increases the system’s efficiency.
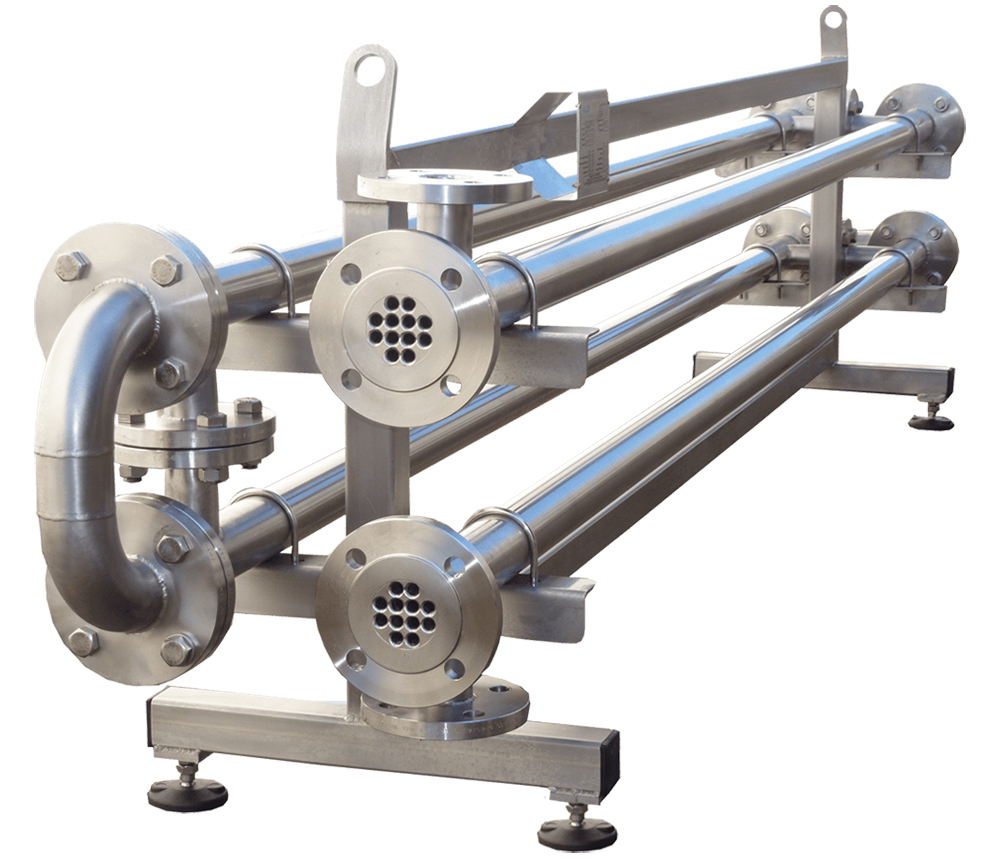
Tube to tube heat exchangers are designed and manufactured in various types to meet the specific operational conditions and demands of the oil and gas industries. Each type has unique features that make it suitable for specific applications. Below is an overview of the types of tube-to-tube heat exchangers, including their operating conditions and features.
This type is one of the simplest tube-to-tube heat exchangers, typically composed of two concentric pipes where the hot fluid flows through one pipe and the cold fluid through the other. Due to its simple structure and ease of cleaning, double-pipe exchangers are used in applications with low flow rates and large temperature differences between the fluids. They are commonly employed in heating and cooling processes within the oil and gas industries.
Features:
Helical tube heat exchangers consist of one or more coiled tubes housed within a shell. Due to the helical design, these exchangers provide a larger heat transfer surface and are ideal for applications requiring high heat transfer rates. Helical tube exchangers are primarily used in energy recovery systems and natural gas processing units.
Features:
Shell-and-tube exchangers are among the most commonly used tube-to-tube heat exchangers. They consist of multiple tubes inside a large shell, where the first fluid flows through the tubes and the second fluid flows through the shell. These exchangers are commonly used in refinery and petrochemical processes, where high temperatures and pressures are required for heat transfer.
Features:
This type of exchanger features fins around the inner tubes to increase the surface area for contact between the fluids and the tubes. Due to this unique design, finned tube heat exchangers are highly suitable for applications that require enhanced heat transfer while minimizing the size and weight of the exchanger. They are frequently used in gas and air heating and cooling units.
Features:
Corrugated tube heat exchangers are made from tubes with corrugated or ridged walls. This specific design induces turbulent flow within the tubes, thereby increasing heat transfer. These exchangers are used in processes that require high-speed heat transfer, such as cooling and heating units in the oil and gas industry.
Features:
Plate-and-tube heat exchangers are composed of a combination of tubes and metal plates through which the fluids pass. The plate design increases the contact surface area between the fluids, leading to improved heat transfer efficiency. These exchangers are highly suitable for applications requiring smaller volumes and higher efficiency, often utilized in oil and gas processes where reducing energy consumption is a priority.
Features:
The materials used in tube-to-tube heat exchangers largely depend on the type of fluid flowing inside and outside the tubes, as well as the system’s operational temperature and pressure. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, nickel alloys, and titanium. Each material has unique properties. For instance, stainless steel is widely used due to its high resistance to corrosion and heat in the harsh environments of oil and gas operations. In high-pressure applications, more durable materials such as nickel alloys are used.
Tube-to-tube heat exchangers are used in various processes within the oil and gas industry. Key applications include:
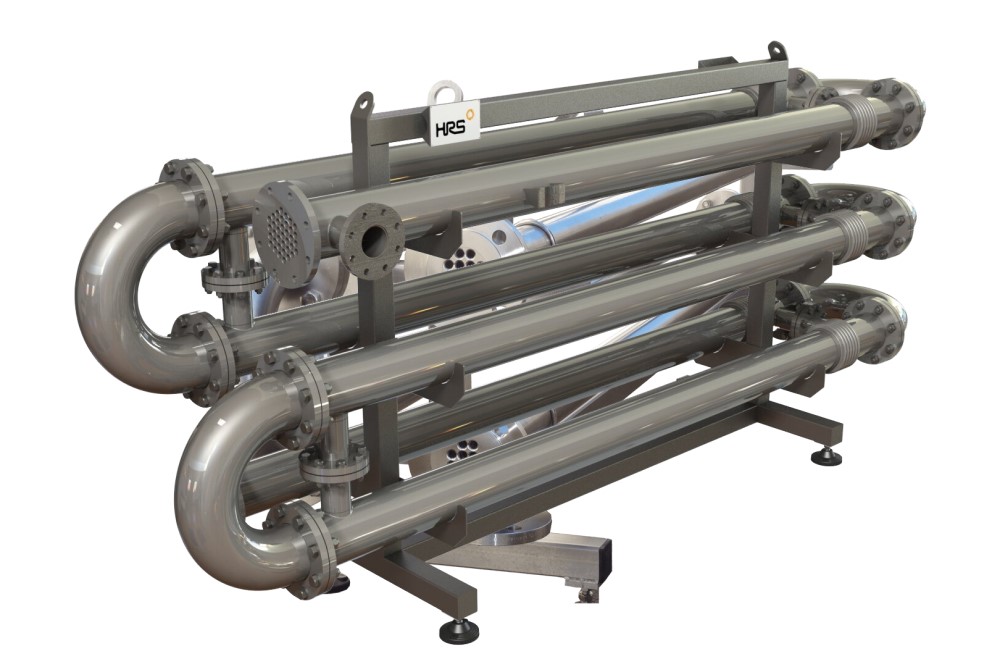

Proper maintenance of tube-to-tube heat exchangers is crucial to maintain their efficiency and prolong their lifespan. These exchangers operate under tough conditions, which can reduce their useful life. Some recommended maintenance practices include:
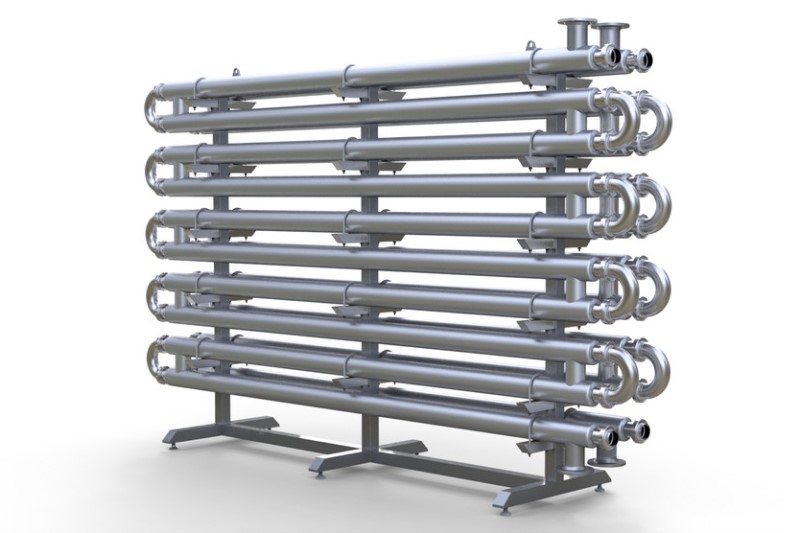
Tube-to-tube heat exchangers are widely used across various sectors of the oil and gas industry. Some of the most significant areas of application include:
Conclusion
Tube-to-tube heat exchangers are one of the most essential components in oil and gas processing systems. Selecting appropriate materials, using them in specific processes, and maintaining them properly all contribute to enhancing their efficiency and longevity. Due to the variety of materials and designs available, engineers can easily integrate these exchangers into different systems.
Petro structure Company is a manufacturer of heat exchangers such as tube to tube exchanger, shell and tube exchanger, plate exchanger and air exchanger. This complex has the possibility of building heat exchangers by using the expert forces and required equipment. Contact our experts for more information.
Sources: